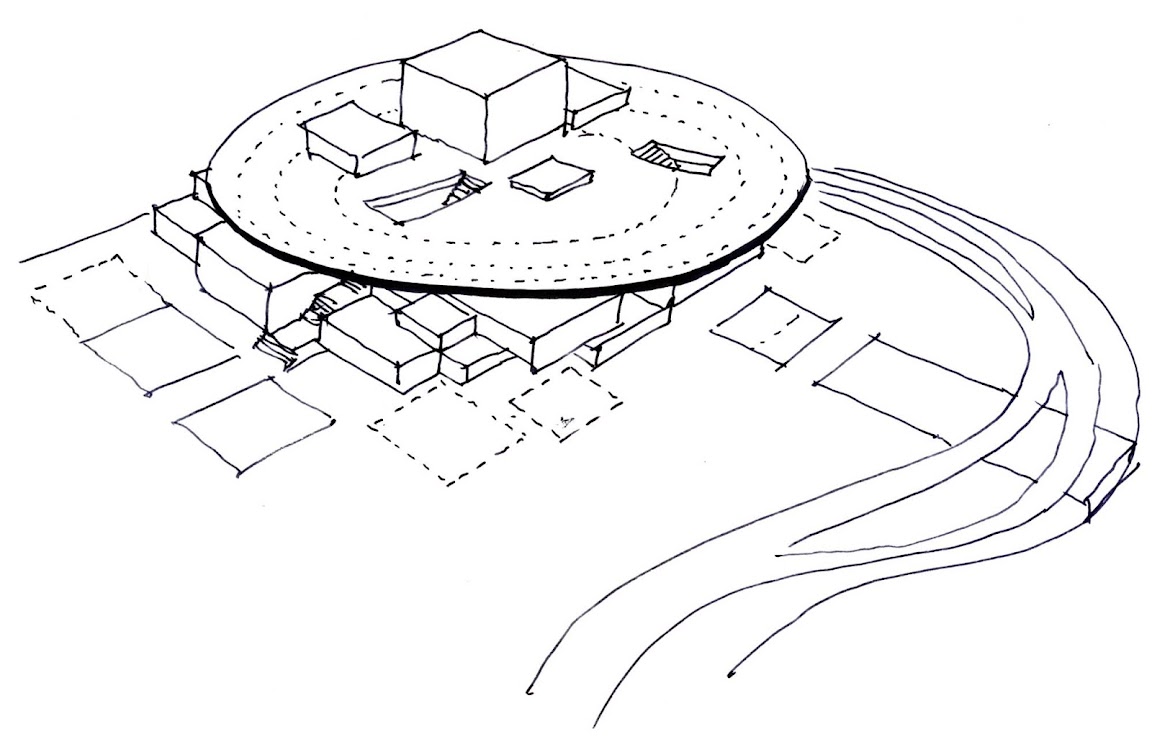
![]()

















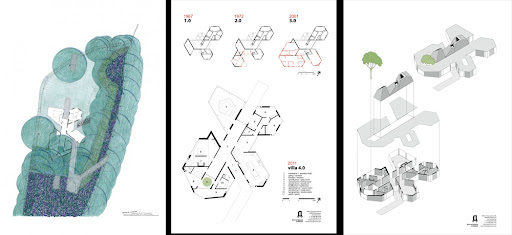
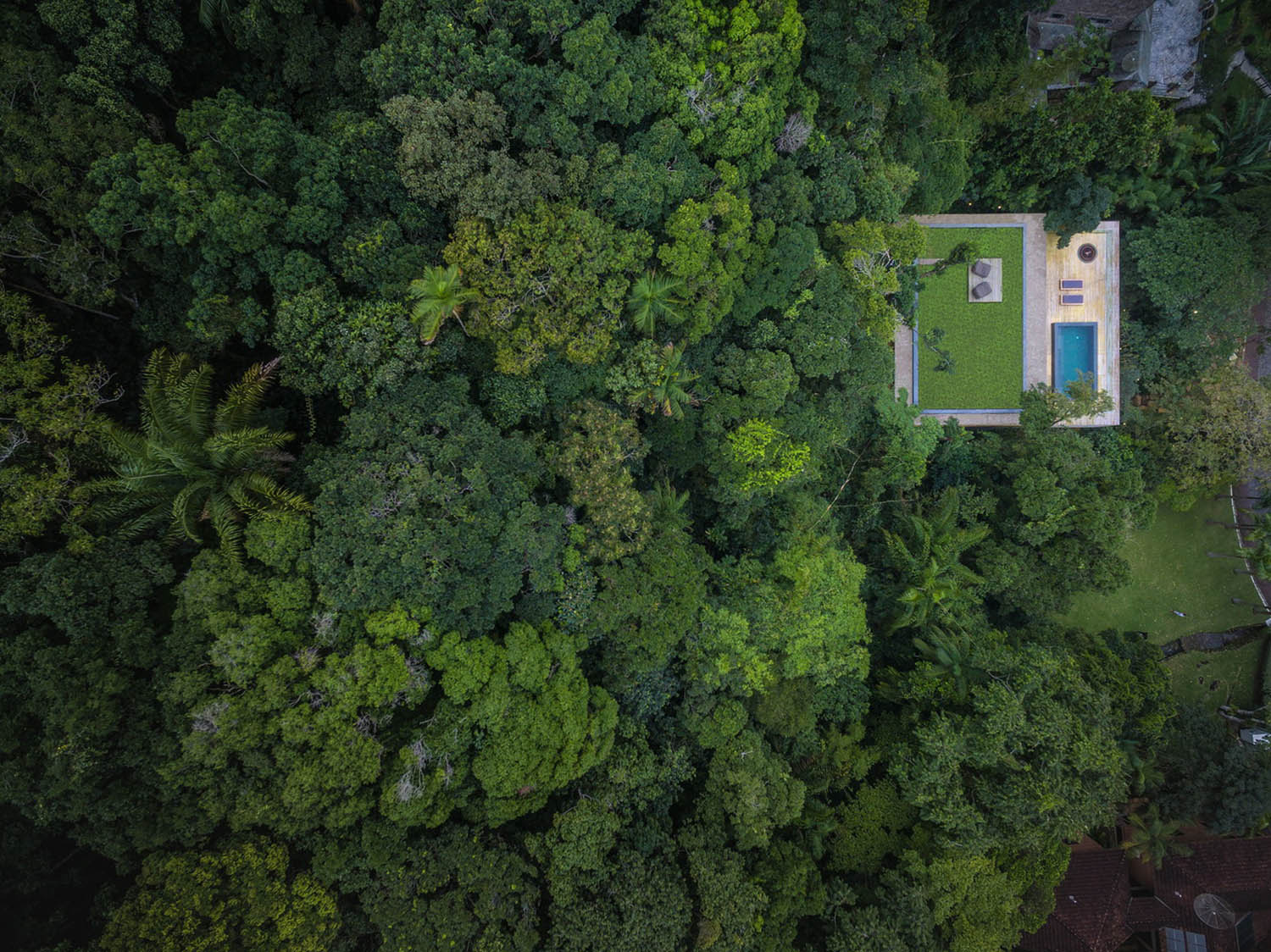
 Architect: Dick van Gameren architecten Location: Netherlands Photographs: Marcel van der Burg – Primabeeld Sustainability is a concept that has been crucial in informing all components of the design, construction and daily use of the house. Rather than create an icon of sustainability, the idea was to consider practically and level-headedly at every step how the house could be least taxing on the environment in both the short and the long term. Key points of departure were maximum reuse of built elements and materials already on site and the use of sturdy and proven techniques to achieve the lowest possible energy consumption. The clients see a sustainable house not as the end of the story but as an inspirational spur to a way of life that places concern for mankind and nature and care of our planet at centre stage. Reuse The design steps off from the existing house, so that along with comprehensively improving the quality of both space and building performance it makes the most of the materials already on site. Components of the existing house that had to be removed have been reused elsewhere in the design where possible. Roofs and facades have been insulated or reinsulated (R Value 3.5). The floor too has been insulated (R Value 3) and finished with a smooth continuous concrete deck floor on compression-resistant insulation. The old wood frames have been replaced with new aluminium-framed facade units of insulated glass (U Value 1.1) Energy and indoor climate A floor heating system has been laid into the new concrete deck floor that can heat or cool the rooms using low temperature heating (water < 35°C). A second system has been installed in the bedroom ceilings to facilitate additional cooling in summer. The entire system is fed by a thermal storage unit. All rooms can be regulated individually. Self-generated energy is not being treated as an option for the time being. The surrounding trees mean that there is much shade for a large part of the year and little wind. The part of the roof that does catch the sun all year long is provided with a solar boiler for hot water facilities (head pipe system). Ventilation of the house is premised on the natural circulation of air throughout the building. Ventilation units in the outer walls make it possible to regulate the exact quantity of air entering the building. In summer, ventilation can be stepped up using a mechanical discharge system in the roof lights of the central hall. Of the two spaces with a lot of glazing, the kitchen has a glass sliding roof and the living room a roof hatch that allows for additional ventilation in warm weather. The ventilation units enable the house to be aired without having to leave windows and doors open. Another source of cooling is by means of a roof-top pump that draws up water from the brook and sprays it onto the roof. The water then flows back into the brook. There is a high efficiency wood burning stove in the kitchen, fuelled with wood from the garden. The heat yield supports the heat pump, thereby reducing the energy consumption of the thermal storage system. The house’s open layout ensures that heat from the stove can spread throughout the house. The living room heats up quickly in winter by being oriented to the south and having all-glass facades, and thus serves as a heat source for the house as a whole. Interior All living spaces receive daylight from more than one direction. Storage units, bathrooms and other ancillary spaces also receive daylight, some of it indirect. All artificial lighting is LED-based. Much of the furniture is built-in and where possible made of sustainable materials: - wood floors and wardrobes: bamboo - kitchen cupboards: Ecoplex (poplar) laminate - settees in the living room and kitchen, curtains in the nurseries: wool filt - floor covering in the sunken sitting area: bamboo Water and garden Rainwater on the roofs is run off directly into the brook. All waste water (greywater) is run off into a tank where it is purified organically and then discharged into the brook. Only biodegradable cleansing agents are used in the house. The new garden layout is informed as much as possible by the replanting of existing trees and shrubs. This gives a greater openness but also more privacy where this is required. The garden is sprinkled exclusively with water from the brook. An electric lawn mower robot keeps the grass at the correct height, and the planting in the garden can be tended without the need for herbicides and artificial fertilizers.
Architect: Dick van Gameren architecten Location: Netherlands Photographs: Marcel van der Burg – Primabeeld Sustainability is a concept that has been crucial in informing all components of the design, construction and daily use of the house. Rather than create an icon of sustainability, the idea was to consider practically and level-headedly at every step how the house could be least taxing on the environment in both the short and the long term. Key points of departure were maximum reuse of built elements and materials already on site and the use of sturdy and proven techniques to achieve the lowest possible energy consumption. The clients see a sustainable house not as the end of the story but as an inspirational spur to a way of life that places concern for mankind and nature and care of our planet at centre stage. Reuse The design steps off from the existing house, so that along with comprehensively improving the quality of both space and building performance it makes the most of the materials already on site. Components of the existing house that had to be removed have been reused elsewhere in the design where possible. Roofs and facades have been insulated or reinsulated (R Value 3.5). The floor too has been insulated (R Value 3) and finished with a smooth continuous concrete deck floor on compression-resistant insulation. The old wood frames have been replaced with new aluminium-framed facade units of insulated glass (U Value 1.1) Energy and indoor climate A floor heating system has been laid into the new concrete deck floor that can heat or cool the rooms using low temperature heating (water < 35°C). A second system has been installed in the bedroom ceilings to facilitate additional cooling in summer. The entire system is fed by a thermal storage unit. All rooms can be regulated individually. Self-generated energy is not being treated as an option for the time being. The surrounding trees mean that there is much shade for a large part of the year and little wind. The part of the roof that does catch the sun all year long is provided with a solar boiler for hot water facilities (head pipe system). Ventilation of the house is premised on the natural circulation of air throughout the building. Ventilation units in the outer walls make it possible to regulate the exact quantity of air entering the building. In summer, ventilation can be stepped up using a mechanical discharge system in the roof lights of the central hall. Of the two spaces with a lot of glazing, the kitchen has a glass sliding roof and the living room a roof hatch that allows for additional ventilation in warm weather. The ventilation units enable the house to be aired without having to leave windows and doors open. Another source of cooling is by means of a roof-top pump that draws up water from the brook and sprays it onto the roof. The water then flows back into the brook. There is a high efficiency wood burning stove in the kitchen, fuelled with wood from the garden. The heat yield supports the heat pump, thereby reducing the energy consumption of the thermal storage system. The house’s open layout ensures that heat from the stove can spread throughout the house. The living room heats up quickly in winter by being oriented to the south and having all-glass facades, and thus serves as a heat source for the house as a whole. Interior All living spaces receive daylight from more than one direction. Storage units, bathrooms and other ancillary spaces also receive daylight, some of it indirect. All artificial lighting is LED-based. Much of the furniture is built-in and where possible made of sustainable materials: - wood floors and wardrobes: bamboo - kitchen cupboards: Ecoplex (poplar) laminate - settees in the living room and kitchen, curtains in the nurseries: wool filt - floor covering in the sunken sitting area: bamboo Water and garden Rainwater on the roofs is run off directly into the brook. All waste water (greywater) is run off into a tank where it is purified organically and then discharged into the brook. Only biodegradable cleansing agents are used in the house. The new garden layout is informed as much as possible by the replanting of existing trees and shrubs. This gives a greater openness but also more privacy where this is required. The garden is sprinkled exclusively with water from the brook. An electric lawn mower robot keeps the grass at the correct height, and the planting in the garden can be tended without the need for herbicides and artificial fertilizers.